
Post Injury Rehabilitation Services
Be Fit Today provides rehabilitation for brain injury clients to assist their recovery through exercise.
Research studies suggests that people with (mild) TBI who exercise show fewer symptoms of Fatigue, cognitive issues and also Depression. Evidence also supports suggestion that exercise stimulates blood flow to the hippocampus segment of the brain.
Through exercise the body builds BDNF, which helps with activities that stimulate mental activity by causing the neurons to branch out and create connections between them. In turn, changes that occur in these synapses between the neuro-pathways are beneficial, as it allows the brain to be stimulated, thus reducing atrophy, along with creating a greater capacity for the retention of information. Essentially, exercise aids in the process of neuroplasticity and helps improve the overall mental mechanisms.
Exercising regularly can help increase the amount of blood that reaches the brain and allows for a rich nourishment of oxygen and nutrients to these cells
Where the effects of brain injury persist or cause problems, a person may be referred to rehabilitation services. Rehabilitation aims to help the brain learn alternative ways of working in order to minimize the long-term impact of the brain injury, and help the survivor and their family to cope successfully with any remaining disabilities.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is defined as an alteration in brain function caused by an external force such as any accident or assault. When a brain injury occurs, damage is inflicted to different sections of the brain including:
- Neurons
- Nerve tracts
If the neurons and nerve tracts are affected, they won’t be able to transmit the messages that tell the brain what to do
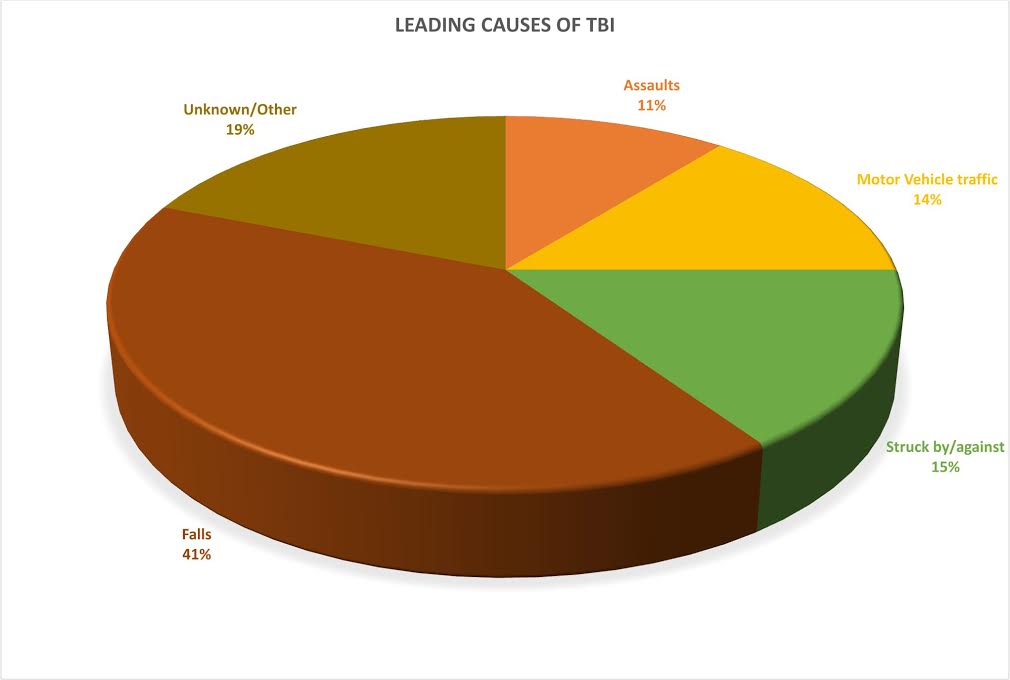
The effects of a traumatic brain injury on an individual depends on a number of factors such as the type, location and severity of injury. Symptoms can be wide-ranging, from physical effects such as balance problems, headaches and dizziness to cognitive, emotional and behavioral effects such as memory problems and anger
TBI can be characterized by the following symptoms:
- Dizziness and loss of balance
- Persisting headaches,
- Prolonged sleeping
- Nausea and vomiting
- Disorientation
- Loss of coordination (in more severe cases)
- Weakness and prolonged numbness in fingers and toes (in more severe cases)
- Clear fluids that drain from the nose or ears (in more severe cases)
- Convulsions and seizures (in more severe cases)
- Concentration problems
